IBM recognized as a Leader in Avasant’s Utilities Digital Services RadarView™ Report 2020 – 2021
Among endless service provider options, novel and disruptive mechanics in innovation brings recognition as a Leader for Utilities Digital Services 2020-2021.
Read the Avasant report
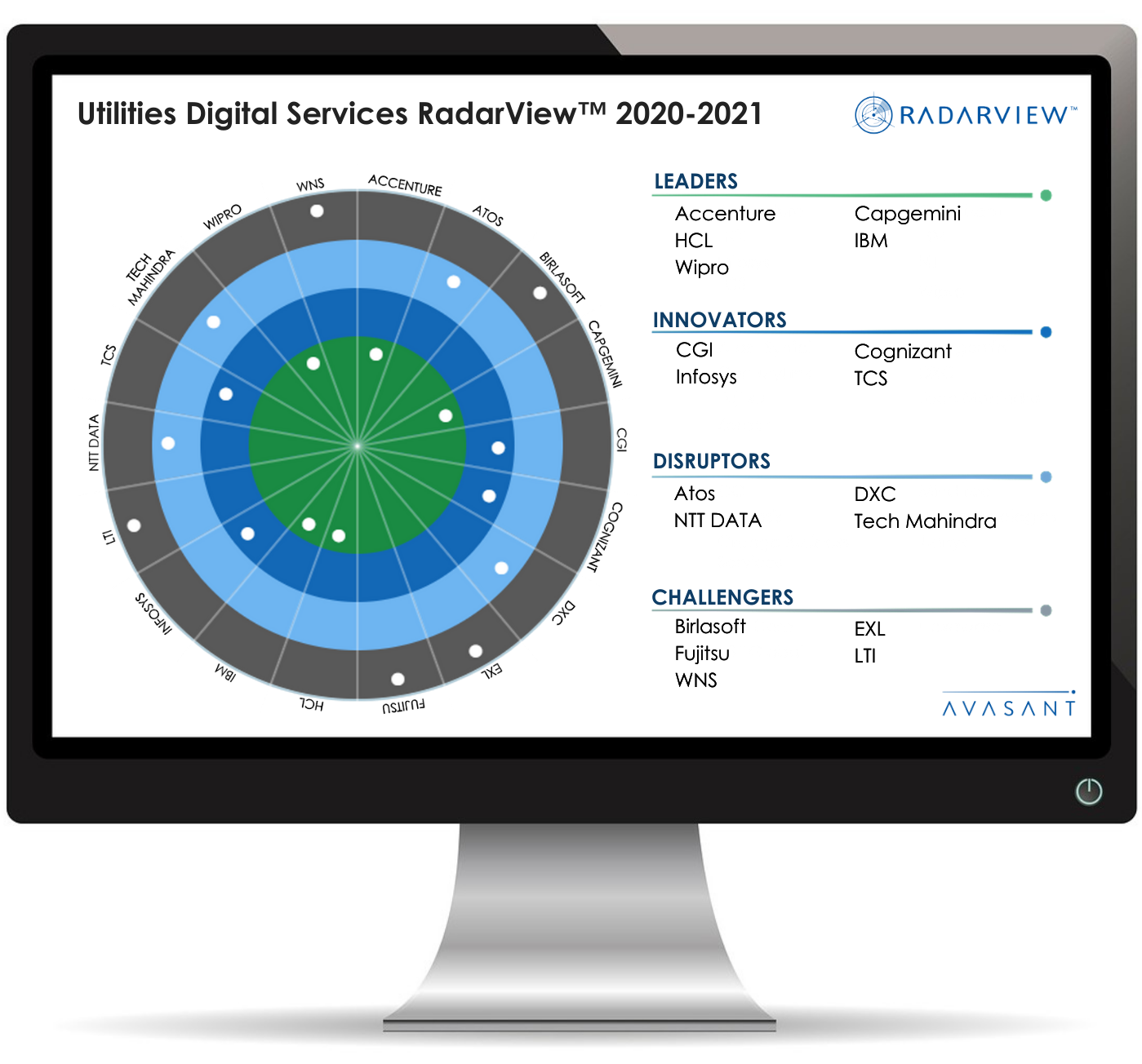
“Invests in start-ups to develop new technology solutions. Leverages expertise from multiple utility specific CoEs.”

AVASANT ANALYST INSIGHTS
Practice Maturity
- IBM focuses on building utility platforms based on micro-services architecture and delivered through cloud. Its utility specific solutions are broadly categorized in 3 areas: network operations (focuses on asset management, smart metering and workforce management), customer operations (focuses on customer billing, digital customer care) and digital enterprise (focuses on BPO solutions, security and cloud migration).
- Cloud is core part of IBM’s business and it plans to develop cloud native cognitive AI capabilities for the utility sector.
- It has marquee products and solutions that are leveraged by other providers. For instance, IBM Maximo is one of the key enablers of digital transformation and is used for asset management and material management in the utilities industry.
- It continuously invests in integrating emerging capabilities and functionalities in its solutions. For instance, its solutions for the utility sector incorporates technologies such as analytics, AI, blockchain, automation and IoT. Its water management solution is a predictive analytics platform for water operations management. Its vegetation management solution leverages predictive analytics with AR/VR for grid operation maintenance.

Investments & Innovation
- IBM looks at acquisitions to get skills that complement its existing capabilities. For instance, it acquired Red Hat to leverage its hybrid cloud capability and migration management solutions in the utilities space.
- It has built multiple utility-specific CoEs across multiple locations. For example, it has a CoE for nuclear power in La Gaude, France, and another for water management in the Netherlands.
- It also has a dedicated research team called ‘Smarter Energy Group’ which conducts research on all aspects of energy supply chain such as energy efficiency, demand management, grid operations, renewable energy management and micro-grids.
Partnership & Ecosystem
- IBM leads the effort to increase adoption and guide the advancement of technology in the utility sector. It launched the Global Intelligent Utility Network Coalition, a group of utility companies working with IBM to accelerate the adoption of smart grid technologies and business solutions throughout the world.
- It actively participated in the creation of applications based on open standards for emerging technologies. For instance, it is a member of Linux Foundation Energy Ecosystem Consortium, which focuses on building scalable applications to transform centralized grids into distributed systems by leveraging open source and open standards.
Featured Resources
IBM’S UTILITIES DIGITAL SERVICES PRACTICE
2019-2020 INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019-2020 HEALTHCARE DIGITAL SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019-2020 AIRLINES AND AIRPORTS DIGITAL SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019 BLOCKCHAIN SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019 SD-WAN MANAGED SERVICES RADARVIEW REPORT
2019 DIGITAL MASTERS RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019 CYBERSECURITY RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019 APPLIED AI AND ADVANCED ANALYTICS RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2019 INTERNET OF THINGS SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2018 HYBRID ENTERPRISE CLOUD SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2018 INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
2018 BLOCKCHAIN SERVICES RADARVIEW™ REPORT
DISCLAIMER:
This graphic was published by Avasant LLC as part of a larger research document and should be evaluated in the context of the entire document. The document is available upon request from Avasant website. Avasant does not endorse any provider, product or service depicted in its research publications, including RadarViewTM, and does not advise users to select only those providers recognized in these publications. Avasant’s research publications are based on information from best available sources and Avasant’s opinion at the time of publication, and their contents should not be construed as statements of fact. Avasant disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including and warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.