Artificial intelligence (AI) solutions are not yet widely implemented, although adoption and investment rates have risen in the past year as many companies look to invest in new capabilities. We expect the adoption and investment rates to continue to rise in the coming years as more IT organizations take advantage of AI capabilities increasingly being embedded in business applications.
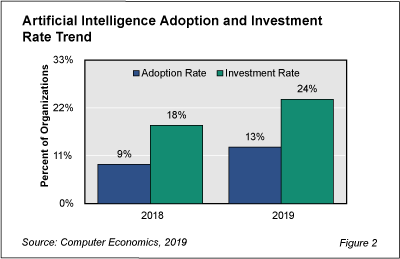
As shown in Figure 2 from our full report, Artificial Intelligence Adoption Trends and Customer Experience, the adoption rate for AI has risen from 9% of all organizations in 2018 to 13% in 2019. During the same period, the percentage of organizations making new investments in AI has risen from 18% in 2018 to 24% in 2019.
Artificial intelligence (AI), as we define it, is not a single technology but several closely-grouped technologies that allow for a machine to absorb and analyze data in order to make a recommendation or take an action. These technologies include rules-based reasoning, machine learning, speech recognition, natural language processing, facial/object recognition, chatbots, and other artificial intelligence capabilities. These technologies are seldom deployed as a separate device or stand-alone system. They are usually embedded as features or capabilities within business applications.
AI is not a particularly new concept. The term was coined in the 1950s and has been a part of life to some extent at least since the 1980s. In terms of public consciousness, however, AI remained in the background until IBM’s Watson won on the game show “Jeopardy” in 2011. Since then, IBM and other companies have been making it a dedicated business strategy to incorporate AI into business processes as an enabling technology.
“AI is especially difficult to track,” said David Wagner, vice president for research at Computer Economics, an IT research firm based in Irvine, Calif. “AI is all around us, and yet generally people do not always realize it. For example, most modern skyscrapers feature elevators that use AI to position themselves best to answer calls before they are made, rather than simply waiting for a button to be pushed on a given floor. But it is ubiquitous, so it does not seem like artificial intelligence. The same can be said for AI in an enterprise setting, whether it is a chatbot, a digital assistant, or a set of rules that govern a network. People often forget that they are interacting with AI once they’ve assimilated it into their lives.”
AI systems can be developed in-house, but many companies simply do not have skills or the budget. Our research bolsters this point. As shown in our full report, far more companies use AI features embedded in business applications rather than develop them in-house. As such, AI as a service is becoming more popular. IBM, as an example, can build sector-specific or company-specific versions of Watson that can digest company data and embed AI into business processes.
The full report provides an overview of artificial intelligence adoption and investment trends, providing data on how many organizations have solutions in place, how many are in the process of implementing it, and how many are expanding implementations. We also look at the return on investment experience, total cost of ownership experience, and considered or planned uses for new AI investment. We conclude with important principles to apply in planning and implementing AI systems.
This Research Byte is a brief overview of our management advisory on this subject, Artificial Intelligence Adoption Trends and Customer Experience. The full report is available at no charge for Computer Economics clients, or it may be purchased by non-clients directly from our website (click for pricing).


