Digital transformation of the procurement function enables enterprises to sail through supply chain disruptions smoothly, improve control and visibility over their spend, and enhance compliance with buying channels and procurement policies. Over 55% of the procurement business process transformation engagements now involve the adoption of digital procurement tools and platforms, and over 40% of procurement engagements involve the adoption of AI and ML capabilities, as noted in our recently published Avasant Procurement Business Process Transformation 2023 RadarView.
The adoption of digital platforms and technologies for procurement processes is not new; enterprises have been leveraging such platforms and technologies for several years to analyze spend, evaluate suppliers, predict risks, and facilitate guided buying.
With the advent of generative AI, enterprises can further automate transactional procurement processes and improve decision-making for strategic sourcing processes. This research byte explores the potential of generative AI in the procurement value chain and how specialist procurement tool vendors are leveraging this technology to improve the potential of their tools.
Potential of Generative AI in the Procurement Value Chain
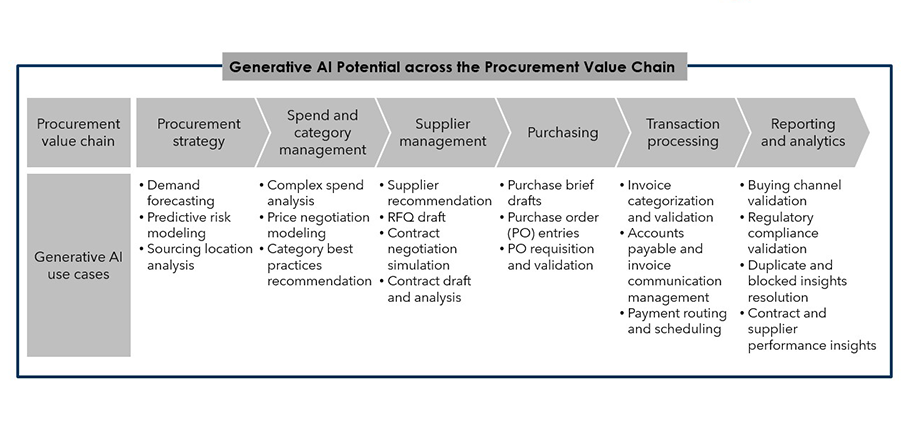
The procurement business function involves trend analysis, content generation, and transaction processing. Given generative AI’s strengths in content generation and complex data analysis, it has the potential to scale up digital transformation across the end-to-end procurement life cycle. Some of the key use cases of generative AI in procurement are listed below.
Generative AI can help enterprises analyze their procurement strategy, contracts, supplier performance, and transactions throughout the procurement life cycle through structured and unstructured inputs. It can also help enterprises draft new contracts and POs, review legal terms, and respond to transactional emails. The existing AI, automation, and analytics technologies are already solving most of these use cases; however, large language models can help enterprises solve these use cases more efficiently without detailed, structured inputs.
Specialist Procurement Tool Vendors Leading the Adoption of Generative AI in Procurement
While most technology vendors have started experimenting with generative AI, specialist procurement technology companies, such as contract management, market intelligence, and accounts payable tool vendors, are taking the lead on generative AI adoption in procurement processes. These tool vendors have already integrated large language models and GPT technology into their solutions to augment digital transformation for the following use cases:
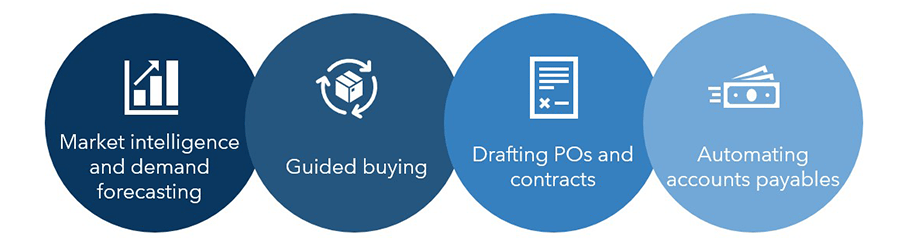
- Market intelligence and demand forecasting: To improve resilience, enterprises must proactively predict and analyze the impact of supply chain constraints such as port blockages and material shortages and macroeconomic factors such as inflation and labor Generative AI can help enterprises analyze large datasets of historical trends and run scenario-based models more efficiently.
For instance, Beroe, a procurement intelligence solution vendor, has integrated ChatGPT into its AI market intelligence assistant to enhance its market analysis capabilities and offer customized recommendations, helping enterprises better predict and plan for market developments.
- Guided buying: Enterprises struggle to improve visibility into their spend, specifically tail spend, due to low compliance or noncompliance with defined buying channels and procurement policies. By analyzing purchase requests, generative AI can recommend preferred buying channels and suppliers to offer an online shopping-like experience, thereby improving compliance. Further, it can help simulate supplier negotiation scenarios by analyzing market trends, pricing benchmarks, best practices, and internal deals databases.
For instance, Globality, an autonomous procurement solution vendor, leverages generative AI in its sourcing bot to automatically recommend best-fit suppliers based on the scope of purchase briefs.
- Drafting POs and contracts: The procurement function involves a lot of time-consuming documentation, such as drafting PR and POs and reviewing RFPs and contracts. As content creation is at the core of generative AI technology, enterprises can use generative AI to quickly draft, review, and analyze such documents, even through unstructured commands.
For instance, Icertis, a contract intelligence solution vendor, leveraged Azure’s Open AI service to augment its proprietary AI data lake to help enterprises review and derive better insights from their contracts.
- Automating accounts payables: Enterprises have been automating transaction-intensive processes, such as accounts payables and invoice processing, for years. With generative AI, enterprises can automate these processes to the next level. For example, even traditionally, enterprises leveraged AI, analytics, and automation to classify accounts payable emails and transactions, among others, but with generative AI’s content generation capabilities, enterprises can suggest responses and automatically respond to transactional requests.
For instance, AppZen, an accounts payable solution provider, launched a generative AI-based solution, AppZen Inbox, to automatically respond to accounts payable emails.
The Way Forward
Integration of generative AI into procurement tools is augmenting the existing digital capabilities of these tools. Such integration presents a multitude of possibilities for future development as it helps enterprises take the next step toward autonomous sourcing and procurement.
However, like every technology, generative AI also comes with its own set of best practices and cautions that enterprises should consider to make the most out of this technology and avoid potential risks. As data sources form the backbone of generative AI, enterprises should prioritize streamlining and integrating their existing enterprise systems to maintain accurate and relevant sources of data before jumping on the generative AI bandwagon. Moreover, using generative AI in an enterprise environment also evokes considerations such as ensuring data privacy and security, addressing algorithmic biases, and maintaining transparency in AI-driven decision-making. Hence, firms should establish mechanisms to constantly monitor their performance in procurement solutions and implement accountability frameworks to address any unintended consequences or ethical concerns and realize the full potential of this technology.
By Ritika Nijhawan, senior research analyst at Avasant