As the baby-boomer generation ages, a growing number of senior IT professionals are retiring. Many organizations have not fully prepared for the loss of so many senior IT professionals in terms of leadership and legacy system support. Furthermore, the demographics within the typical IT shop are changing, leading to a number of “generational issues” between IT workers. These generational issues represent the differences between older IT workers and younger IT workers in regards to technology, culture, business focus, and compensation. The differences are often substantial–especially as perceived by IT management.
This Research Byte is an executive summary of our full report, Planning for the Coming Wave of IT Staff Retirements. The full report describes how IT organizations are planning to deal with these issues. It also analyzes the differences, as perceived by management, between the skills and business focus of younger versus older IT workers. Finally, it provides recommendations for managing the transition to a new generation of IT leaders.
The Generational Shift Is Already Underway
In early 2007, Computer Economics surveyed over 150 IT senior managers and executives concerning the transitional workforce issues that they anticipate will accompany their baby-boomer retirements. This Research Byte summarizes the results of that survey. It describes how IT executives plan to deal with the pending retirements of so many skilled IT professionals, and it analyzes their perceptions of the IT skills and business focus of younger IT workers (defined as under age 40) versus older IT workers (age 40 and up).
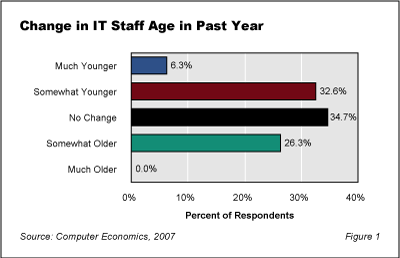
Our survey found that the demographic shift to younger IT staff members is real. In order to establish a baseline on age difference, we asked our survey respondents to tell us whether their IT staff was younger or older than it was 12 months ago.
As shown in Figure 1, there is a noticeable shift toward a younger IT staff in many organizations. Almost 40% of our survey respondents indicate their IT staff is younger this year, while only 26% indicate it is somewhat older. Although this change may be the result of a variety of factors, it undoubtedly includes some baby-boomer retirements. As the baby-boomer exodus from the IT workforce continues, the shift toward a younger IT staff will certainly accelerate. As this occurs, IT management must consider how this will impact their ability to support existing systems and processes.
Our survey also found that the shift to younger workers is most pronounced in larger organizations. When IT staff age is viewed at more granular level, it is clear that large companies will bear the brunt of the transition to a younger IT workforce. (Throughout this study, we define large companies as those with revenues over $1 billion, medium companies as those with revenues between $500 million and $1 billion, and small companies as those with revenues under $500 million.)
Large companies have a much higher percentage of older IT workers than medium and small companies do. This is probably because larger companies tend to have more legacy systems (especially running on mainframes) which are traditionally the domain of older IT staff members. This means that as baby-boomer retirements accelerate over the next few years, large companies are likely to have more severe transitional issues than their smaller counterparts.
Content of the Full Report
In the full version of this report, we analyze the anticipated effect of baby-boomer retirements by organization size. We then analyze the popularity of five strategies being employed by IT organizations to deal with the loss of senior IT personnel:
- Legacy system replacement
- Succession planning
- Outsourcing
- Alternative employment arrangements (e.g. contracting)
- Enticements to defer retirement
We then analyze the perceptions of our survey respondents regarding the skills and characteristics of older versus younger IT workers in seven dimensions:
- Technical skills
- Technical flexibility
- Compensation requirements
- Team orientation
- Communication skills
- Business focus
- Work ethic
Finally, we outline a five-step approach for planning and managing the transition to a new generation of IT leadership.
May 2007
This Research Byte is a brief overview of our report on this subject, Planning for the Coming Wave of IT Staff Retirements. The full report is available at no charge for Computer Economics clients, or it may be purchased by non-clients directly from our website at https://avasant.com/report/planning-for-the-coming-wave-of-it-staff-retirements-2007/ (click for pricing).