The recent frenzy of interest in generative AI has changed the perception of artificial intelligence. Once locked inside other processes, AI was often forgotten as it powered everything from IoT devices, automation, and security. But generative AI shined a new light on AI, not as an embedded technology, but as a driver of efficiency, automation, and creativity. Despite low adoption statistics to date for AI, we predict that is about to change.
For this report, our annual Technology Trends 2023 survey was designed and deployed before the explosion of interest in generative AI in late 2022. It was thus not called out specifically as a category in our survey, although elements of it—specifically natural language processing and machine learning—were included.
Nevertheless, at the time of this survey, AI was still not finding quite as much traction as one would expect. As shown in Figure 2 from our full report, AI Adoption Trends and Customer Experience, the adoption rate for AI is 18% of all organizations in 2023, down from 25% in 2022. During the same period, the percentage of organizations making new investments in AI dropped from 39% in 2022 to 28% in 2023.
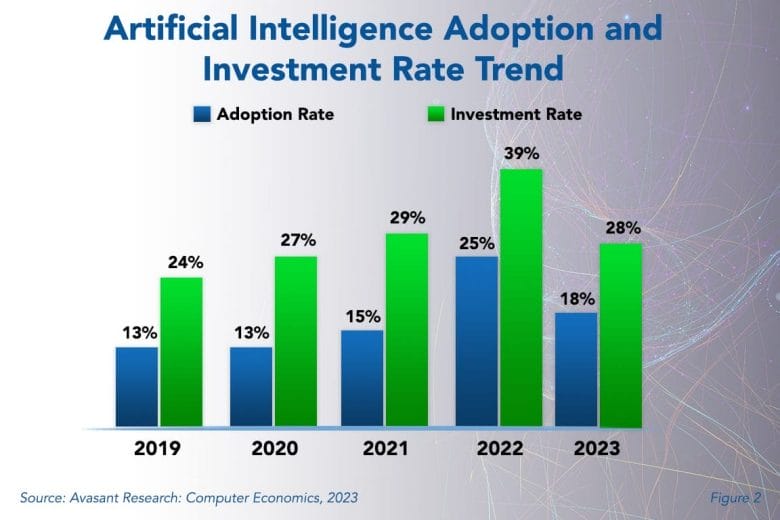
The figure shows that, on the surface, it seems most companies have not yet realized the use cases that would lead them to invest heavily in AI. But we expect that to change in the coming months and years.
The AI frenzy was started in late 2022 by OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an AI bot that can create human-like responses to a user’s questions or instructions. Being freely available for anyone to experiment with, it wasn’t long until enterprises were using it for documentation, report writing, and other projects that required a creative hand. Since OpenAI made ChatGPT generally available at no charge in November 2022, it is the fastest technology in history to reach 100 million users.
It was not until ChatGPT took off that dozens of companies either launched their own generative AI tools or ramped up work on their own large language model (LLM) projects. In addition to many smaller players, Microsoft released its Bing chatbot (also based on OpenAI) and Google rolled out Bard, based on its LaMDA model. Meta’s CEO Mark Zuckerberg said in a Facebook post that Meta is “creating a new top-level product group at Meta focused on generative AI to turbocharge our work in this area.”
Opinions on the current state of generative AI vary widely. Some say it will help all manner of people, from students, to teachers, to professionals, to doctors, engineers, and researchers. However, AI has been prone to inaccuracies, including outright falsehoods, known as “hallucinations,” and most AI chatbots do not cite sources for their information, leading to misappropriation of intellectual property. In one widely reported incident, Samsung suffered when sensitive documents were leaked because employees unwittingly exposed them to ChatGPT.
“Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize business,” said Tom Dunlap, director of research for Avasant Research, based in L.A. “But only if it’s used wisely and judiciously. Companies need to be aware of the issues with generative AI and take steps to mitigate them.”
AI, as we define it, is not a single technology but several closely grouped technologies that allow a system to absorb, analyze, produce, and learn from data in order to make a recommendation or take an action. These technologies include rules-based reasoning, machine learning, speech recognition, natural language processing, facial/object recognition, and other capabilities. They are seldom deployed as stand-alones and are usually embedded as features or capabilities within business applications.
Our full report provides an overview of AI adoption and investment trends, providing data on how many organizations have solutions in place, how many are in the process of implementing it, and how many are expanding implementations. We also look at the return-on-investment experience, total cost of ownership experience, and considered or planned uses for new AI investment. We conclude with important principles to apply in planning and implementing AI systems.
This Research Byte is a brief overview of our report on this subject, AI Adoption and Customer Experience. The full report is available at no charge for subscribers, or it may be purchased by non-clients directly from our website (click for pricing).