What is Private LTE and How Is it Different from Wi-Fi?
Private long-term evolution (LTE) is a local wireless communication network that operates on the LTE technology but is owned, operated, and used by a private organization or an individual. The key difference between private LTE and Wi-Fi is spectrum ownership, which can be licensed, unlicensed, or shared. Wi-Fi typically operates in an unlicensed spectrum, meaning multiple Wi-Fi bands can operate on the same frequency band and are more suited for smaller-scale environments.
Unlocking the Benefits of Private Wireless Networks
Private wireless networks are needed to support mission-critical applications where uninterrupted communication is needed. It is usually needed in places with higher network coverage areas, making it more suitable for large industrial and remote sites. Hence, it is widely used in manufacturing, utilities, transportation, and public safety industries, where a dedicated and secure wireless communication infrastructure is necessary. It brings in the capabilities of supporting Industry 4.0 initiatives by providing operational technology (OT) connectivity.
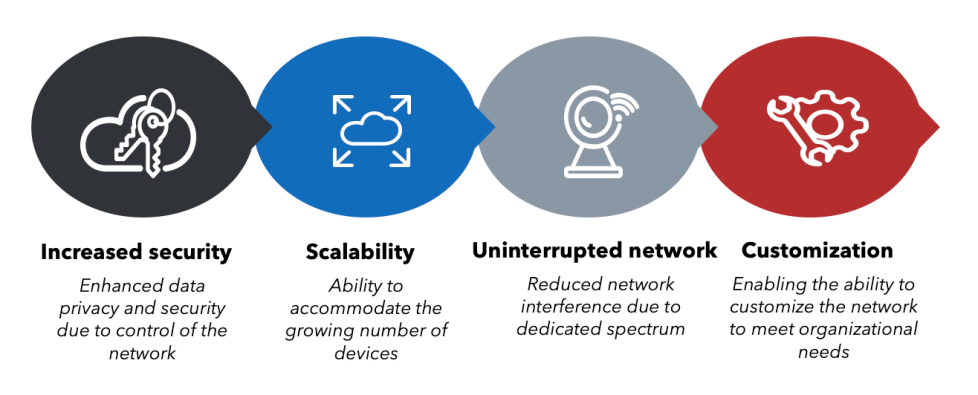
Below are the key benefits of transitioning to a private LTE network:
Key Factors for Clients to Assess When Choosing Private Wireless Networks
Private wireless networks are critical for asset-intensive industries focused on driving IT-OT convergence. The following are a few factors that need to be evaluated for an enterprise to decide whether to switch to private LTE:
-
- Performance: Private LTE can offer better performance for companies that have business applications with high bandwidth and low latency and those that require real-time data transmission in areas such as control and coordination of industrial machinery, smart grid operations, and manufacturing operations control systems.
- Security: Private LTE has more robust security features, including encryption and authentication features. This minimizes the risk of exposure to data transmitted through IoT devices.
- Area of coverage: Private LTE is more suited for larger areas such as industrial facilities and factories located in remote regions where Wi-Fi connectivity can be an issue.
It is important for enterprises to make an informed decision on whether switching to a private wireless network is the right move for them based on the organization’s needs.
The Wireless LTE Ecosystem
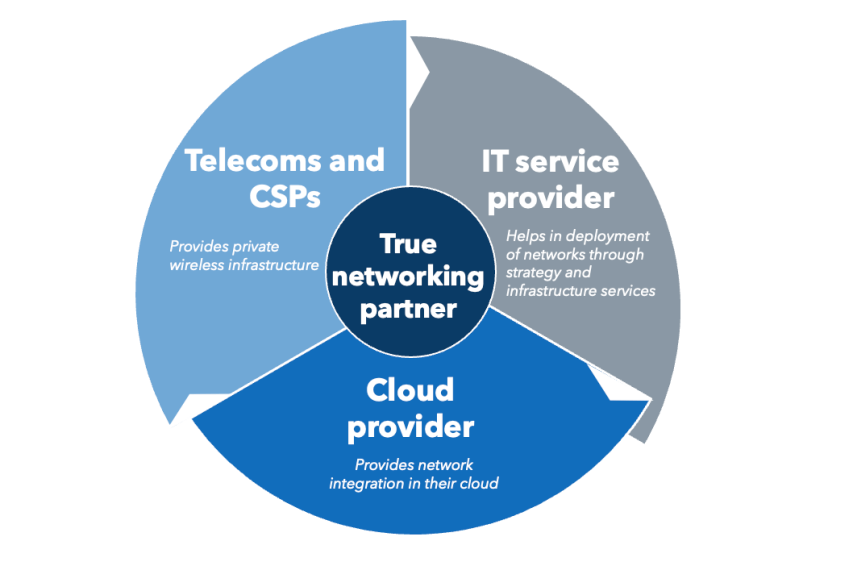
To determine if adopting a private LTE network aligns with a company’s strategic goals and to ensure a smooth transition that maximizes benefits, companies should forge alliances with the right technological collaborators. The following are the three key categories of partners necessary for the successful implementation of private LTE:
-
- Telecoms and communication service providers (CSPs): They bring in the core IP for setting up infrastructure needed for private networks. Some of the key vendors include the likes of Nokia, Ericsson, AT&T, Comcast, Orange, Telefónica, Verizon, and T-Mobile.
- IT service providers: There are multiple IT service providers in the market providing private wireless services ranging from strategy, design, and implementation to governance. Some of the key players are Accenture, Capgemini, DXC, Kyndryl, and NTT DATA.
- Cloud companies: To enable network scalability and agility, cloud platform companies enable enterprises to run network workloads on the cloud. The three major cloud platform companies, Amazon Web Services, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, offer private LTE cloud services.
Role of Service Providers in Private Wireless
IT service providers bring cross-industry experience and expertise in developing end-to-end solutions. They act as a true advisory partner by devising a business case for industries and identifying the cost benefits of moving to a private wireless network and the right networking model for operations. They bring together an ecosystem of their existing alliances with CSPs, cloud platforms, and telecom companies, which gives them access to the right talent pool with the right expertise.
Case in Point: DXC Signal, a Private LTE and 5G Offering
The market hosts a variety of service providers providing private wireless network services, including DXC Technology’s bespoke offering, DXC Signal Private LTE and 5G, which caters to the private wireless network sector. This solution integrates Nokia’s Digital Automation Cloud and Nokia MX Industrial Edge with DXC’s proprietary Platform X™ to create a robust network operations center. At its core, DXC Signal can oversee and administer client-specific private LTE networks via the intelligent automation capabilities of Platform X. In collaboration with Nokia, DXC delivers managed services aimed at aiding industrial enterprises in their digital transformation and expediting their Industry 4.0 efforts. DXC has facilitated the deployment of private LTE solutions for diverse industry clients across sectors like shipbuilding, energy, oil and gas, and industrial manufacturing.
Strategizing for Private Wireless Future
Businesses must recognize that the shift to private wireless goes beyond simply upgrading from Wi-Fi—it’s a strategic move for sectors prioritizing automation and digital transformation to meet Industry 4.0 benchmarks. It’s crucial for these enterprises to partner with experts who can provide a thorough cost-benefit analysis for private network implementation. Given the expansive growth of the IoT landscape, heightened security demands, the scaling of industrial operations, and the increasing criticality of uninterrupted connectivity, the demand for private wireless solutions is set to intensify.
By Parinita Singh, Research Leader, Avasant